RIF Marketplace Architecture
The RIF Marketplace at its core is composed of a set of smart contracts deployed on the Rootstock (RSK) blockchain, a read-only cache for performance and scalability, and a front-end (UI) which allows users to easily connect, browse available services and features, and interact with other participants. Each specific RIF service node (RIF Services) must connect to the Marketplace Smart Contracts, listen for the required events, and ensure a proper interaction and provision of that service to the End-user.
The diagram below shows an overview of the RIF Marketplace architecture, which is explained next:
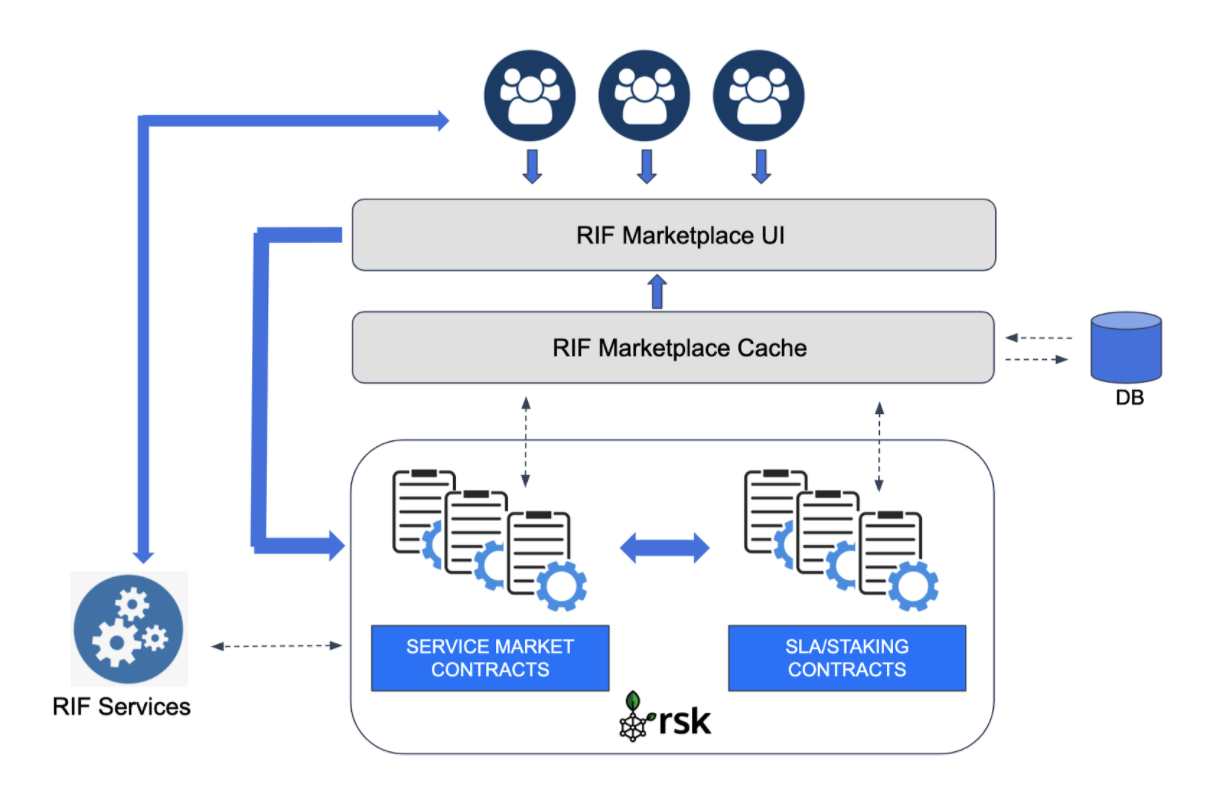
RIF Marketplace is built around 3 core components:
UI-Frontend Dapp
End-Users interact with the RIF Marketplace through the main Marketplace Dapp (RIF Marketplace UI). This web application presents information about the service categories available, allows users to browse/search for specific providers, and allows providers and consumers to engage in service agreements. It also allows Providers to register their offered services and track their performance and current customers, manage their staking, among other functionalities.
Cache
The information presented in the UI comes from RIF Marketplace Cache. This component is always listening to the blockchain, and synchronising a database with the information from the smart contracts organized in a readable and optimized way. Its main objective is to improve the performance, scalability, and overall user experience of the RIF Marketplace. It is important to note the Cache can be reconstructed at any time from the information available in the Blockchain, and is accessible only in read-only mode providing information to the UI, but not modifying or altering any information on the smart contracts in any way.
Smart Contracts
The blockchain layer consists of a set of Smart Contracts deployed on the Rootstock (RSK) blockchain, and are divided into two main groups: Those related to buying/selling the specific RIF Service being offered (ie: Storage, Name Services, Communications, etc), and those related to common modules and activities of the RIF Marketplace such as the staking, slashing, SLAs, and dispute resolution mechanisms. These smart contracts are related, and interact with each other to ensure correct synchronization and agreements between each other.